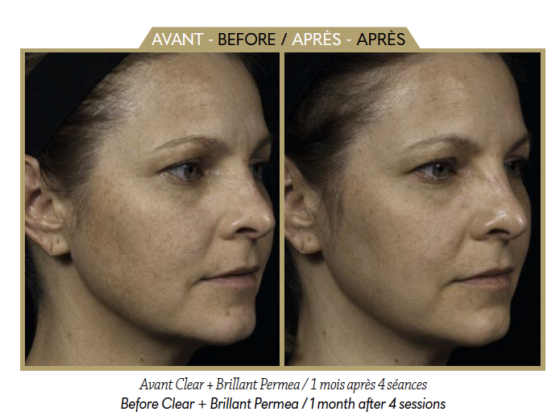
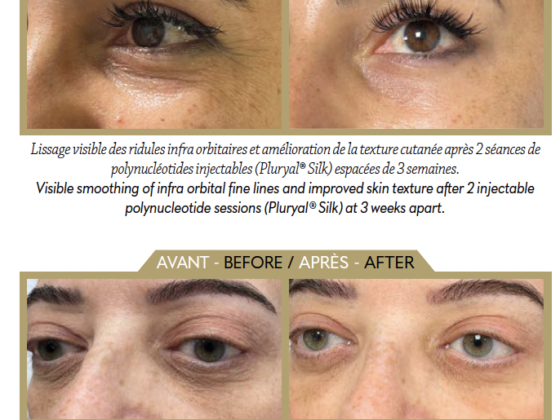
Dr Eric Pujos
From collage peptides to aesthetics treatments: how to stimulate skin regeneration and reduce the signs of aging.
Essential to the structure and elasticity of the conjunctive tissue of all the organs, collagen is the most abundant microprotein in the human body. Its fibril structure with a triple helix of polypeptides dotes it with resistant and elastic properties.
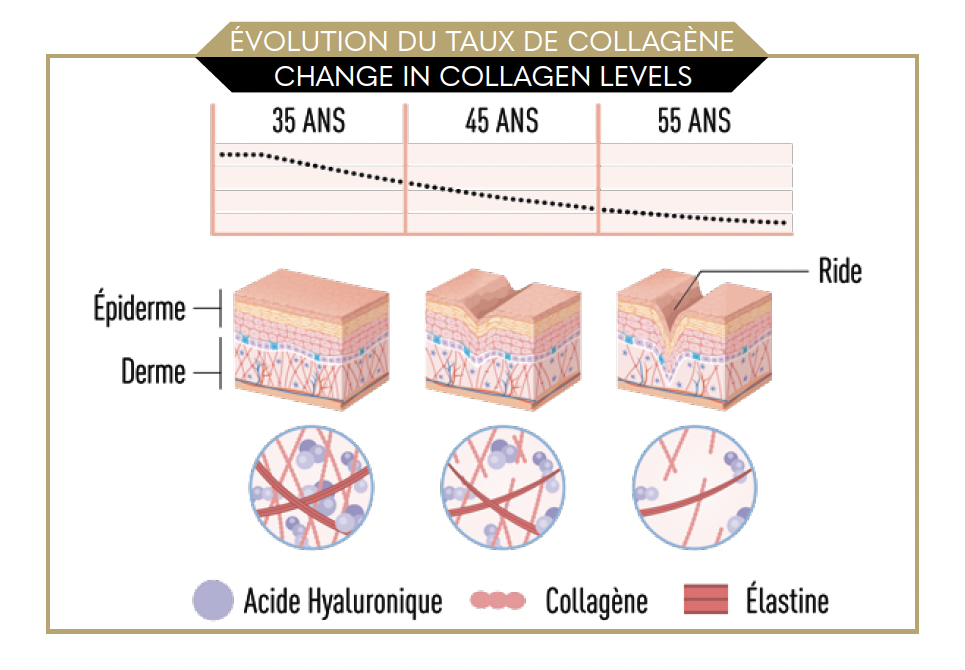
The fibroblasts’ synthesis of endogenous collagen reduces by 1% per year from age 25 onwards. The main signs of this tissue reduction are wrinkles, dry and sagging skin, joint pain, and an increased risk of bone fractures and muscle injuries. All of these signs of collagen deficiency are accentuated by oxidative stress (pollution, sun exposure, smoking, advanced age, infections, etc.). Collagen supplementation is therefore extremely useful for slowing down skin aging (the heaviest organ in the human body) and preserving the muscles and joints. To understand supplementation, let us start with its mechanism of action.
Mechanism of action(1)
Collagen is synthesised by the fibroblasts, cells in the extracellular matrix of the conjunctive tissue, which play a crucial role in tissue repair. The peptides penetrate the fibroblasts thanks to the membrane transporters. They are activated by the growth factors then used in collagen fibre synthesis (1).
Growth factors also trigger a cascade of biochemical reactions in the endoplasmic reticulum (including mRNA transcription), using glycine and proline to synthesise the alpha chains (2). These alpha chains join together in a triple helix to form procollagen (3), which is then transported to the extracellular matrix (4). The ends of these procollagen molecules are cut off by the peptidases, leaving tropocollagen molecules (5) that are crosslinked thanks to the influence of lysyl oxidase and then activated by its co-factor, vitamin C (6), to form collagen fibres (7). The exogenous provision of collagen peptides through oral supplementation guides its endogenous production by the fibroblasts.
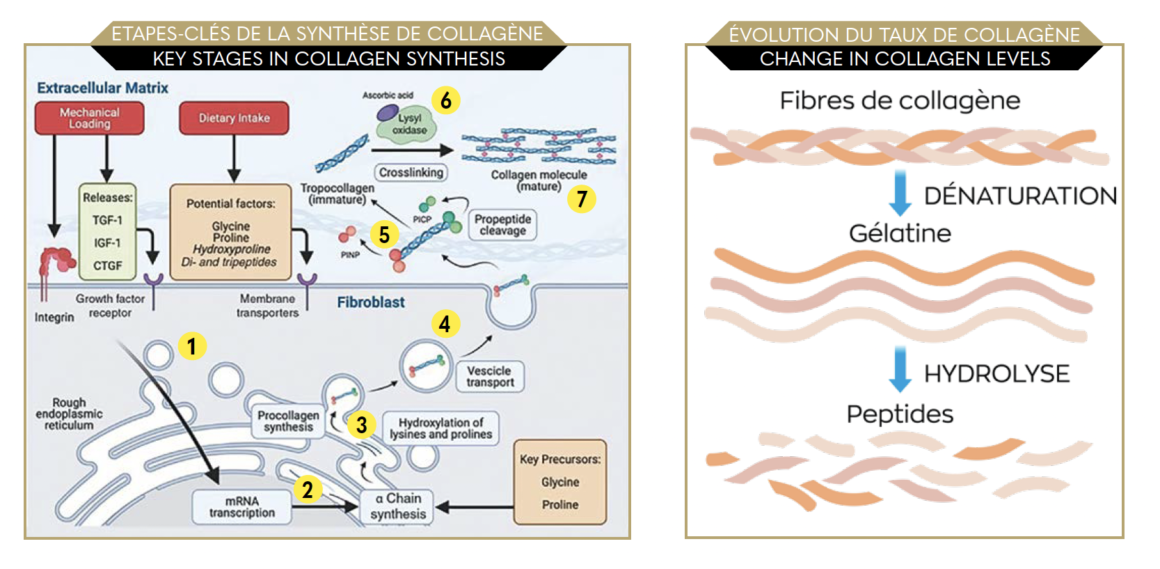
Collagen supplementation
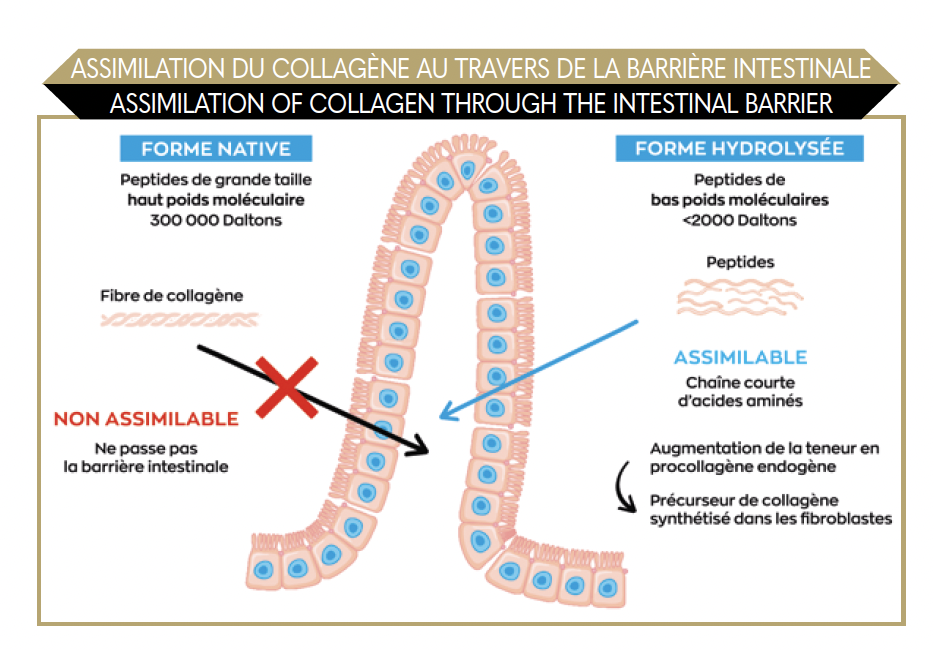
A number of clinical studies, as well as a meta-analysis (2), have shown the significant effect that collagen peptide supplementation can have: a dose of 1g/day improves the skin’s hydration, while a dose of 3g/day primarily improves its elasticity. From 5g/day, the anti-aging and anti-wrinkle effects are even more noticeable. At 10g/day, we see up to a 35% reduction in wrinkles (2). It has also been shown that it has an effect on musculoskeletal and bone issues: up to 40% less joint pain with a dose of 10g/day (3). However, in its native form, collagen is a protein with a high molecular weight (300,000 Daltons) that is difficult to absorb through the intestine. It needs to be hydrolysed and transformed into much smaller peptides (<2,000 Daltons) that can pass through the intestinal wall and be used by the fibroblasts. Oral supplements must therefore contain collagen peptides that can be used immediately by the body in the conjunctive tissue.
These low molecular weight peptides pass through the intestinal barrier into the bloodstream, then penetrate the fibroblasts thanks to membranal transporters activated by the growth factors (TGF-1, IGF-1, CTGF) and are then used for the synthesis of collagen fibres. Marine collagen, which comes from fish skin, bones and scales, is the best type of collagen to take. Its molecular structure is the best tolerated and most easily assimilated. What is more, it is suitable for specific diets (Halal, Kosher).
It also has the advantage in that it has no connection with the transmission of zoonotic diseases.
To make it easier to take and monitor, several galenic formulations have been developed. Dry formats to be taken orally, in particular powders, are most suitable for large doses (>5g/day) as the dosages are straightforward (1 to 2 times per day). Liquid forms (blisters, shots) are ready to use and have a suitable texture for high doses (5 to 10g/day). Tablets and capsules are best for doses of between 1 and 3g/day, as they have a neutral taste and a very handy format. A minimum course of 3 months is recommended. Collagen supplements should not be taken with food.
Advantages of collagen peptides combined with medical aesthetics procedures. Taking collagen peptides potentiates the effects of medical aesthetics procedures that aim to stimulate the body’s synthesis of endogenous collagen:
• It increases the hydrophilic action of hyaluronic acid in order to plump the skin for the long term.
• It potentiates the collagen production triggered by the insertion of tensor threads, thus enhancing the lifting effect.
• It optimises laser and radiofrequency treatments by speeding up skin regeneration.
• It helps speed up healing post-peel by stimulating the fibroblasts and reducing inflammation.
In conclusion, oral collagen supplementation is needed to slow down aging in all of the organs, but particularly the skin. There are rules to follow in order to supplement correctly: namely, to take collagen peptides with a low molecular weight (between 200 and 2,000 Daltons) and of marine origin.l
Bibliographie / Bibliography
(1) Nutrition Reviews – 2022 – The impact of collagen protein ingestion on musculoskeletal connective tissue remodeling: a narrative review.
(2) Int J Dermatology – 2021 – Effects of hydrolyzed collagen supplementation on skin aging: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
(3) Etude clinique réalisée en triple aveugle, en 2020, sur un groupe ayant pris 10 g de collagène Naticol® vs placebo, réalisée durant 12 semaines, auprès de 50 participantes.
(4) The effect of collagen peptides on the reduction of join pain: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
Dr Eric Pujos

President of France Médecine Esthétique, FME. Doctor, Medical speaker specialising in body contouring and aesthetic medicine.