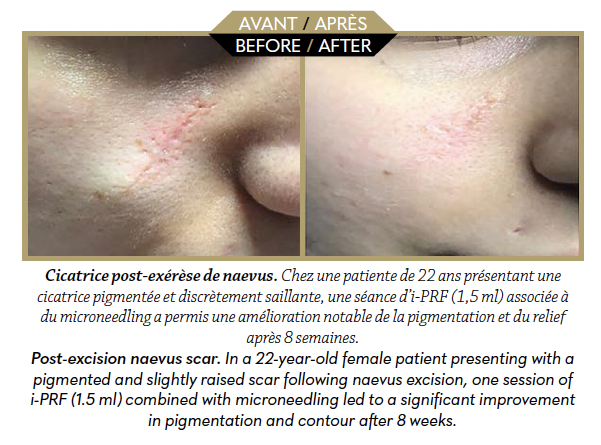
A combined, natural and targeted strategy to durably reduce traumatic, surgical or inflammatory skin scars.
PRP, i-PRF and microneedling together stimulate the biological mechanisms of skin repair. This personalised approach improves the texture, suppleness and appearance of scars, with progressive and natural results.

Dermal regeneration and scar biology
Cutaneous wound healing is a tightly regulated process involving a dynamic succession of complex biological events. The phases of hemostasis, inflammation, cellular proliferation and tissue remodeling contribute to the restoration of the structural and functional integrity of the skin. Any disruption in this cascade may lead to pathological scarring. These disorders include excess collagen deposition (hypertrophic and keloid scars), aberrant neovascularisation or a disorganised extracellular matrix (atrophic scars). The goal of modern therapeutic strategies is to induce high-quality skin repair, mimicking as closely as possible the histological characteristics of healthy tissue. In this context, autologous platelet concentrates (PRP, i-PRF) combined with microneedling represent an innovative approach—both biological and physical.
PRP: rapid activation of trophic cascades
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) is obtained from whole blood centrifuged after the addition of an anticoagulant. When injected directly into the dermis, platelet activation occurs naturally due to the physiological calcium present in the tissues, making the exogenous addition of calcium gluconate unnecessary. This activation triggers platelet degranulation and the release of multiple growth factors. Among these, PDGF (platelet-derived growth factor) promotes chemotaxis and fibroblast proliferation, TGF-β (transforming growth factor beta) regulates collagen synthesis and inhibits metalloproteinases, while VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) stimulates angiogenesis.
PRP exerts a rapid trophic effect, with a peak release occurring within the first hours post-application. This kinetic profile makes it ideal for initiating tissue repair processes, particularly in recent or inflammatory scars. Additionally, interactions between PRP and endothelial and epidermal cells enhance reepithelialisation and perilesional vascular remodeling.
i-PRF: three-dimensional matrix with sustained release
Injectable Platelet-Rich Fibrin (i-PRF) is obtained without anticoagulants through gentle centrifugation, preserving platelets, leukocytes, and mesenchymal cells within a lightly coagulating plasma. Once injected, i-PRF gradually polymerises into a three-dimensional fibrillar matrix, acting as a reservoir for trophic factors.
Unlike PRP, i-PRF ensures continuous release of bioactive signals for 7 to 10 days. This sustained activity promotes deep neocollagenesis, progressive resolution of inflammation, and a reduction in local oxidative stress. The fibrillar architecture also provides a scaffold for cellular migration and dermal tissue reorganisation.
i-PRF is particularly suited for mature, fibrotic, or keloid-prone scars, where prolonged stimulation is required to restore tissue homeostasis.
Microneedling: a generator of endogenous repair signals
Microneedling is a collagen induction technique based on the creation of micro-channels in the skin using motorised devices. This micro-perforation induces mechanical stimulation of fibroblasts, local cytokine release (IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α), and activation of TGF-β-dependent pathways. Microneedling reactivates endogenous repair mechanisms while increasing transcutaneous permeability. Combining this physical stimulation with the application or injection of PRP or i-PRF creates a therapeutic synergy, enhancing intradermal diffusion of active factors and amplifying their biological effects.
Physiological result: organised dermal remodelling
The combination of these three techniques targets the different layers of scar tissue simultaneously. PRP initiates repair, i-PRF maintains a pro-regenerative microenvironment, and microneedling activates resident cells. This strategy promotes:
• increased synthesis of type I collagen and reduction of type III,
• homogenisation of dermal density
•reduction of dystrophic microvasculature,
• improved pigmentation,
• and enhanced tissue flexibility.
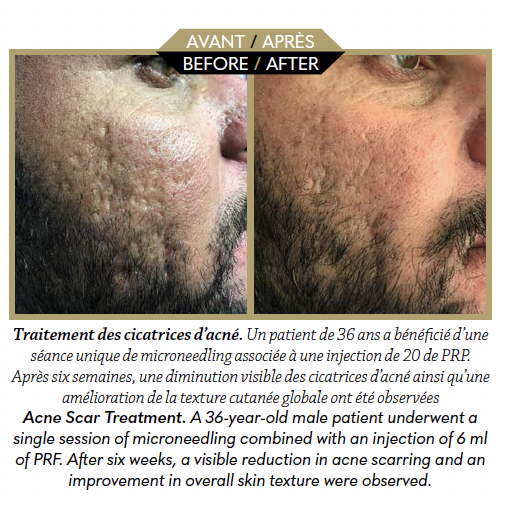
The effectiveness of the combined treatment becomes visible from the second or third session, with progressive improvement over 3 to 6 months. The protocol is well tolerated, without major adverse effects, and can be tailored to the scar type and patient skin phenotype. PRP, i-PRF and microneedling form an effective combination to improve complex scars. This regenerative, safe and personalised approach offers natural and durable results by activating the intrinsic mechanisms of skin repair.
Dr Nina Hassani

Dr. Nina Hassani practises general and aesthetic medicine with a strong focus on regenerative therapies in the Swiss canton of Jura. A graduate of CIMEL, she is recognised as an expert in autologous regenerative medicine and serves as a founding and board member of the International Multidisciplinary Society for Applied Regenerative Medicine (IMSARM).
More: cardiomed-beaute.ch