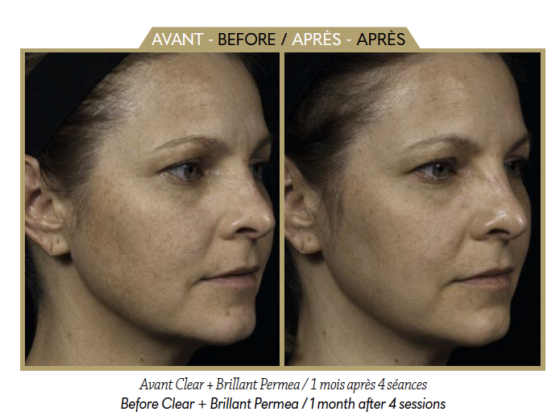
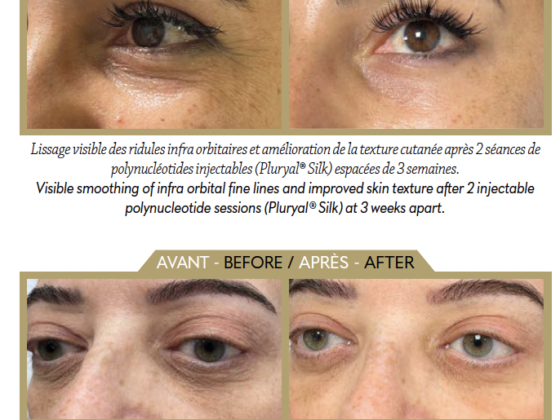
When I started out as a morphological and anti-aging doctor, making my patients happy by beautifying their features was my main concern. But I very quickly realised that they needed more than a little “boost of freshness”: it is one thing to age beautifully, and another to age “beautifully, healthily and in great shape”. And the Covid-19 pandemic has only confirmed this need to stay healthy, strengthen our immune defences and detoxify the body.

First of all, I will go through a few notions that I believe are essential to carrying out this modest task in the vast field of micronutrition.
1. The human microbiota is defined as the groups of micro-organisms present in a tissue, whether they are commensal or symbiotic, discretionary or obligatory pathogens: bacteria, viruses, parasites and fungal species.
2. Oxidative stress: This is the accumulation of oxidative lesions following an imbalance between the formation and destruction of free radicals. It alters our cells’ components.
3. Immunity: The body’s defence mechanisms against external elements, in particular infectious agents (viruses, bacteria or parasites). The body’s defences are based on: the integrity of its barriers, innate immunity and specific immunity. Its barriers are made up of several key actors: the skin, the respiratory epithelium, the pulmonary alveoli, the intestinal barrier, the microbiota. The enemies of immunity are: uncontrolled inflammation, hyperinsulinism, oxidative stress, dysbiosis and intoxication by chemical substances (heavy metals, pesticides).
4. Hepatic detoxification : This is a highly complex process that involves several reactions and contributors, with great individual variability and adaptability to the environment, lifestyle and genetic character of each individual. Thanks to hepatic detoxification, the lipophilic toxins are transformed into hydro soluble components that can be eliminated by the kidneys and the urinary excretory system. Toxins are mainly accumulated in the fat, the brain and the liver (hepatic steatosis: “fatty liver”). There are many reasons for this accumulation of toxins: heavy metals, endotoxins, hormones, pesticides, pollution, solvents, medicines, preservatives, allergies and intestinal hyperpermeability. The body’s main emunctories are: the digestive system, the urinary system, the respiratory system, the skin and the mucous membranes.
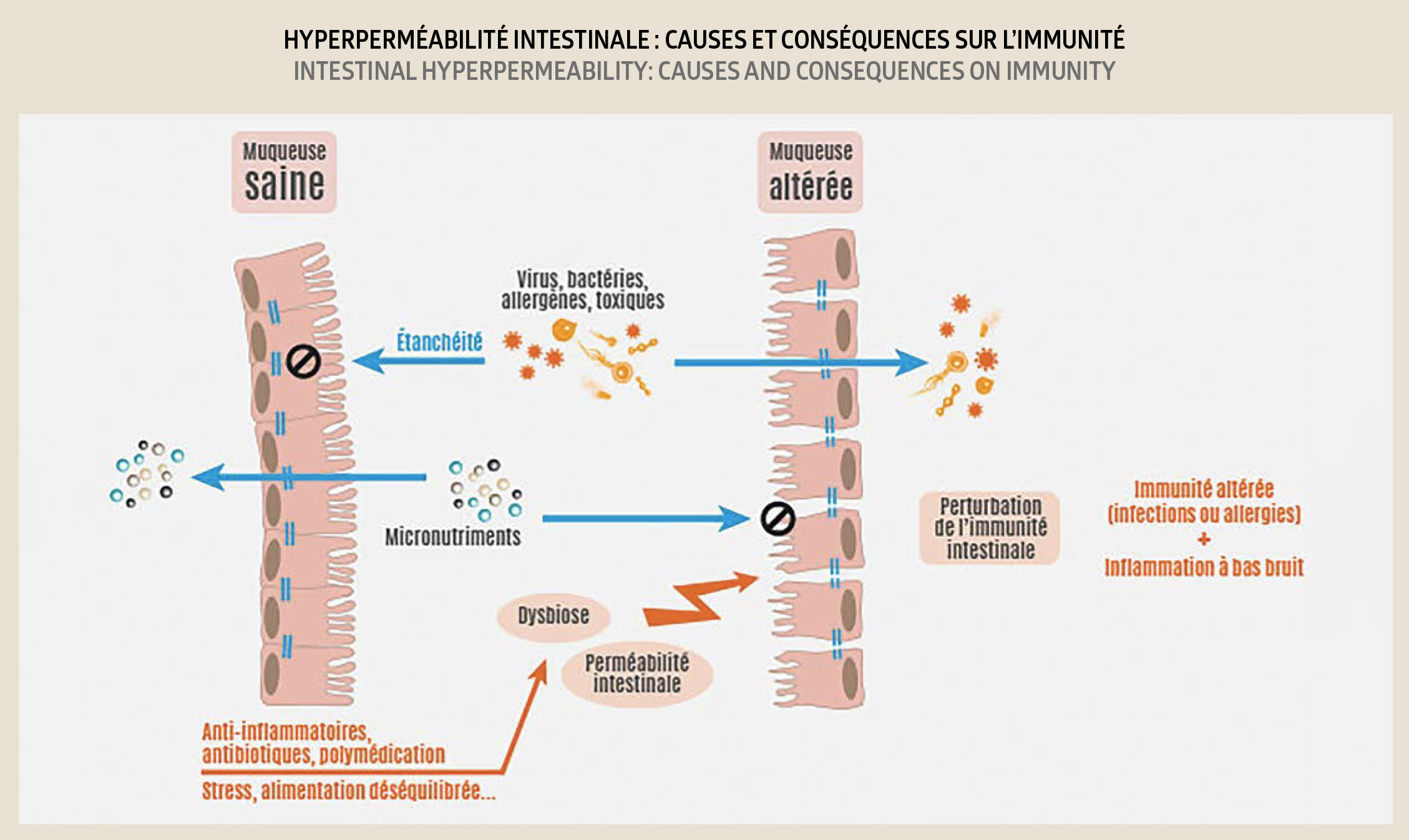
5. Leaky Gut Syndrome
The intestinal barrier is formed by contiguous cells that regulate its permeability/impermeability. When the integrity of the intestinal mucous membrane is compromised, this function is deregulated. The microbiota is disrupted. Toxins are no longer able to pass through properly and the liver is forced to work overtime in order to treat this excess of toxins. The human body enters a state of increased systemic inflammation.
How to strengthen the immune defences
Strengthen the barriers, chew properly, combat oxidative stress, restore omega 3 and 6 levels.
The Mediterranean diet can be used as a reference model, as it promotes the action of the 5 As:
• Antioxidant: vegetables (artichoke, avocado, turnip, spinach, broccoli, red cabbage, peppers), fruit (red berries, goji berries, citrus fruits), cereals, legumes, grains and oil seeds, green tea
•Anti-inflammatory: oily fish, all fruit and vegetables, rapeseed oil, nut oils, linseed oil, olive oil, camelina oil, tea
• Anti-hyperglycaemic: vegetables (seaweed, avocado, chard, mushrooms, fennel, soya, etc.), fruit (red berries, citrus fruits), unrefined cereals, vinegar
• Anti-toxin: organic foods
• Anti-dysbiosis: probiotics (yoghurts and fermented milk, fermented soya, lacto-fermented vegetables) and prebiotics (fruits with skin, tubers, cereals, all vegetables, legumes).
Food supplements and trace element boosters:
• L-glutamine to strengthen the intestinal barrier
• Probiotics and prebiotics
• Vitamin D, which is vital for immunity
• Turmeric, the gold-standard anti-inflammatory
• Vitamin C for its antioxidant properties
• Zinc, essential for the smooth functioning of certain stages of the immune reaction
How to boost hepatic detoxification
Hygiene and dietary rules and supplements:
A number of symptoms can lead to a diagnosis of toxin accumulation: diffuse and unexplained muscle pain, chronic fatigue, fibromyalgia, food allergies or sensitivity to chemical products.
Folates are essential for the physiological rollout of hepatic detoxification. The highest folate levels are found in eggs (72.2%), cow’s liver (55.7%), orange juice (21.3%), cabbage (6%), beans (4.5%) and lettuce (2.9%). Alkalinisation of the urine (lemon juice, vinegar) promotes the urinary excretion of toxins that have become hydro soluble.
Vegetables: beetroot (provides methionine which helps eliminate toxins) is good for the liver and intestine, artichoke stimulates the secretion of bile, which is good for the liver, asparagus has a diuretic action which stimulates the urinary excretion of toxins, black radish is a great antioxidant that promotes the drainage of the bile and hepatic ducts.
• Coenzyme Q10 is a real mitochondrial booster
• Betaine promotes hepatic stimulation
• Desmodium has a hepato-protective action
Micronutrition for great skin: does beauty come from the inside?
Our skin is actually a double agent: it plays the role of the primary barrier against aggressions but also reflects what is going on inside our body.
This means that taking care of the skin’s integrity and quality – protecting it from ionising radiation, hydrating and nourishing it with antioxidants (especially vitamin C serum and vitamin E) – helps to improve the quality of this primary barrier.
It is also vital to keep the intestinal flora balanced and detoxify the liver to fight against certain skin flaws or calm any symptoms that chronic autoimmune diseases might present on the skin. We want to beautify the skin: not only its external appearance, but our body as a whole.
Appendix
It is also vital to fight against an accumulation of heavy metals. But what does this mean? Metals are not created or destroyed by the body. They tend to accumulate in the soil, soft water and sediments. They include: arsenic, tungsten, nickel, beryllium, antimony, platinum, cadmium, caesium, aluminium, lead, barium, tin, copper, uranium, thorium, mercury, thallium. The accumulation of these heavy metals in the body affects the cytochrome oxidase, several kinases, haemoglobin and myoglobin. They are real poisons for the mitochondria and detoxification factors. They have been proven to play a role in certain forms of Alzheimer’s disease.
Références :
- Conférences du Pr CASTRONOVO, Nutrihealth, université d’été, Aout 2019 ; chapitres 7 et 9
- Les maladies chroniques vers la 3ème médecine, Pr André Grimaldi, Yvanie Caillé, Frédéric Pierru, Didier Tabuteau
- Vitamin D : its role and uses in immunology ; Deluca HF, Cantorma MT. FASEB J. 2001 Dec
- Nutrition and immunology : from the clinic to cellular biology and back again. Chandra RK. Proc

By the doctor Limaiem Joumni Wided
Doctor Limaiem practises aesthetic & preventative anti-aging medicine in Paris 15. She works in the A&E department of Longjumeau University Hospital. Emergency doctor at the Estrée clinic, Stains 93.
More information on dr-limaiem-esthetique.fr